Model Sliding: A Logical Approach to AI Model Selection
Model Sliding is a proof-of-concept use of logic that employs a unique transition between different AI models based on the nature of the prompt and task at hand. This dynamic model selection strategy optimizes AI performance by matching each task with the model best suited to handle it - GPT-3.5-Turbo or GPT-4.
The application uses a logical dictionary of specific keywords associated with each task type to determine the most suitable model. If the prompt doesn’t match any specific keywords, the application defaults to a predetermined model.
The Model Sliding method offers an interactive and user-friendly interface. Users can interact with different models by simply typing their prompts or tasks. The assistant avatar and model information dynamically update in response to the chosen model, providing real-time feedback and enhancing user experience.
Include your Fine-Tune Model, the logic is built in to refine optimal responses.
Meta Model Sliding: A Proof of Concept for Dynamic Model Selection
In an era where artificial intelligence is rapidly advancing, there is an abundance of AI models, each with its unique strengths and specializations. Leveraging these strengths for specific tasks can significantly enhance performance. However, the challenge lies in switching seamlessly between these models, ensuring that each task is handled by the most competent model.
To overcome this challenge, we introduce the concept of “Model Sliding”. This proof-of-concept application demonstrates a novel approach toward logical model selection, capitalizing on the strengths of each model for optimal responses and use of tokens.
Here are the roles that the Assistant will use. Example responses for different assistant roles:
Meta Model Sliding Assistant Examples
- Code Assistant
Other roles include:
-
Storytelling Assistant
-
Writing Assistant
-
Social Media Assistant
The Logical Challenge
- Is there a more cost efficient and logical way to use different GPT models for various tasks? And can it be seamless?
Model Sliding: An Overview
Model Sliding allows for the transition between different AI models based on the task at hand. The underlying principle of this approach is to maximize the potential of each model for specific tasks.
- GPT-3.5-Turbo could be favored for generating Python code.
- GPT-4 might be the go-to for crafting engaging social media content.
The Meta Model uses a set of keywords to determine which model is best suited for the task. The keywords are associated with specific models and tasks, enabling the Meta Model to “slide” between models as per the requirements of the task.
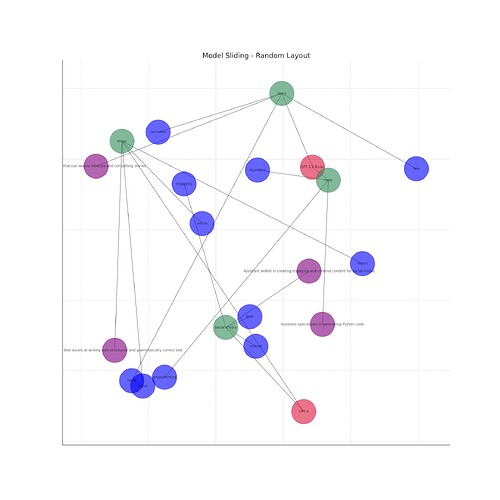
Visualizing Model Sliding
To better understand the concept of Model Sliding, we have visualized it as a network of nodes, where each node represents a model, task, role, or keyword. The edges connecting these nodes signify the relationships between these elements. The various task dimensions are represented by different colors. A neural network of layers can be seen at the core of the network, representing the models.
The network visualizations below show the Model Sliding network in different layouts. The models (GPT-3.5-Turbo and GPT-4) are at the core, connected to various tasks like ‘code’, ‘story’, ‘essay’, and ‘social media’. These tasks are further linked to other keywords and the roles they play.
In these network visualizations, the models (GPT-3.5-Turbo and GPT-4) are at the core, connected to various tasks like ‘code’, ‘story’, ‘essay’, and ‘social media’. These tasks are further linked to other keywords and the roles they play.
Advantages of Model Sliding
Model Sliding offers several benefits:
- Task-specific Optimization: By allocating the most appropriate model for each task, Model Sliding enhances performance across a wide array of tasks.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Instead of concurrently operating multiple models, Model Sliding leverages one model at a time, ensuring efficient use of resources.
- Adaptability: The system can be effortlessly updated to incorporate new models and tasks as they emerge.
- Optimal Token Usage: With the ability to dynamically select models based on the task, Model Sliding ensures optimal use of tokens. This is especially advantageous when multitasking or engaging with large language models (LLMs), as it allows for effective token allocation, leading to enhanced performance and cost efficiency.